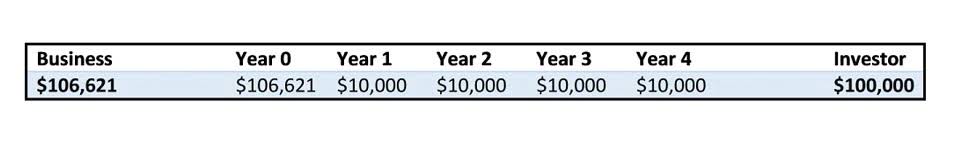
The Annuity Formula for the Present and Future Value of Annuities
If you do go for one, just make sure you pay close attention to the fees, avoid the more exotic variations, and don’t take out a bigger contract than you really need. With this option, you can set the payment to be made at the end of the period (ordinary annuity) or the beginning of each period (annuity due). Investing in a variable annuity involves risk of loss – investment returns and contract value are not guaranteed and will fluctuate. Mathematically, that adjustment involves multiplying the result by the discount rate plus 1. You can see this by comparing the two present value formulas below.
What Is the Formula for the Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity?
Unless you also selected a joint life annuity, and your partner survives you. Do you need, or prefer, the certainty of a guaranteed retirement income with your pension annuity in advance savings? You have the right to shop around with your personal pension fund. You do not need to take an annuity with the same company you saved your pension with.
How much income will I receive from my lifetime annuity?
If you’re invested in a With Profits Fund, a Market Value Reduction (MVR) may apply when you take your retirement benefits. This MVR could be more, or less, than the pension providers illustration. Taking your fund on the pension plan’s stated retirement date may avoid this reduction.
Use Our Free Instant Annuity Calculators & Tools…
- In other words, with this annuity calculator, you can compute the present value of a series of periodic payments to be received at some point in the future.
- The higher the discount rate, the lower the present value of the annuity.
- Usually, the income is initially set up with an ‘emergency tax code’.
Many annuities come with a surrender fee, which you incur if you try to take a withdrawal within the first few years of your contract. Typically, the surrender period lasts between six to eight years, although they’re sometimes even longer. These fees can be on the large side, so it’s hard to back out of a contract once you sign on the dotted line. Ordinary annuities are better for the payer, while annuities due are better for the payee.
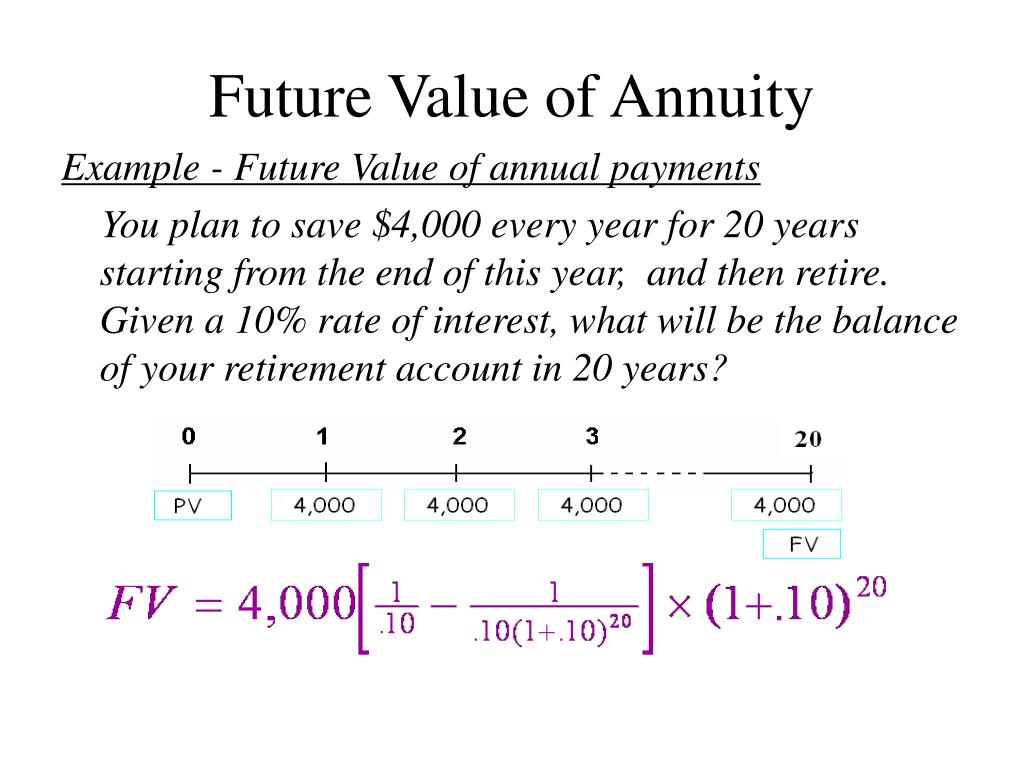
In this section, you can learn how to use this calculator and the mathematical background that governs it. The easiest way to understand the difference between these types of annuities is to consider a simple example. Let’s assume that you deposit 100 dollars annually for three years, and the interest rate is 5 percent; thus, you have a $100, 3-year, 5% annuity. The term “annuity due” means receiving the payment at the beginning of each period (e.g. monthly rent).
Should I get a joint lifetime annuity?
Other annuity contracts may allow the withdrawal of the gains (not principal) from an annuity without penalty. Also, as retirement accounts, annuities allow early withdrawals without penalty under certain situations. For example, the annuitants become disabled, suffer a major medical emergency, or are diagnosed with a terminal illness. In addition, some contracts offer benefits for using penalty-free withdrawals to pay for long-term care expenses.
An indexed annuity is invested in market indexes like the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Because these indexes include many of America’s top companies, they generally reflect the shape of the economy as a whole. Like a variable annuity, an indexed annuity is designed to keep pace with inflation and secure your purchasing power for life. Financial calculators also have the ability to calculate these for you, given the correct inputs. These recurring or ongoing payments are technically referred to as annuities (not to be confused with the financial product called an annuity, though the two are related). Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, so the person would come out ahead by choosing the lump-sum payment over the annuity.
It is calculated using a formula that takes into account the time value of money and the discount rate, which is an assumed rate of return or interest rate over the same duration as the payments. The present value of an annuity can be used to determine whether it is more beneficial to receive a lump-sum payment or an annuity spread out over a number of years. If you have selected a joint life annuity, the annuity transfers to your spouse, partner or financially dependent partner following your death. However, when you buy a lifetime annuity, you’ll have a cooling off period, usually 30 days, in which to change your mind. After this time, you cannot alter or cash in your annuity if you decide it is not right for you.